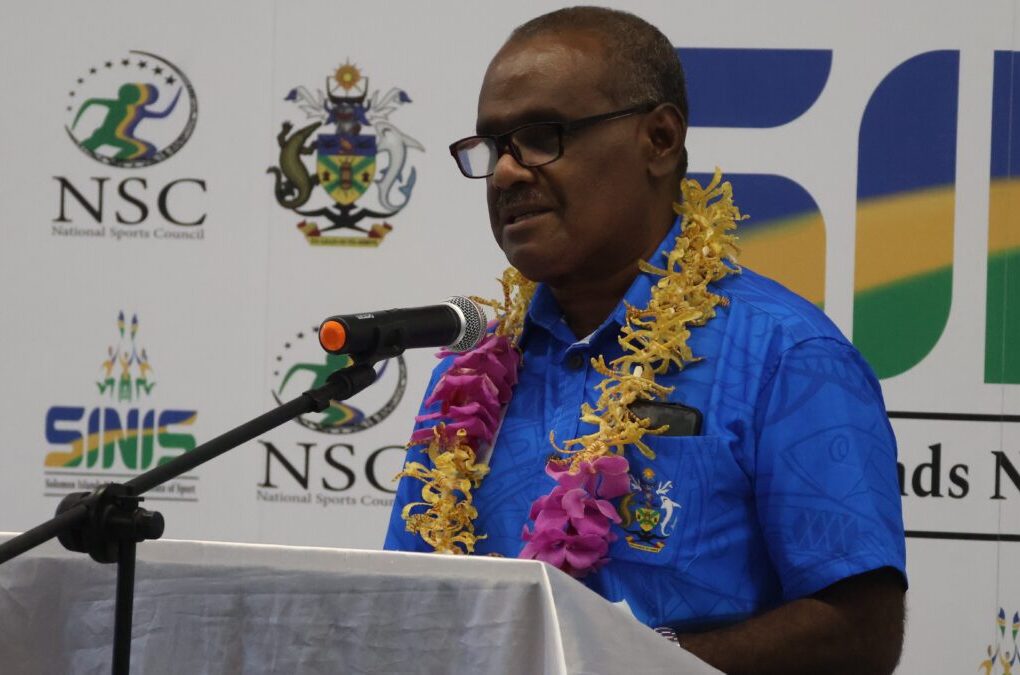
SINIS is the People’s Legacy from the 2023 Pacific Games: Solomon’s PM
Honiara, Solomon Islands – Friday, 09 May 2025 – Prime Minister Hon. Jeremiah Manele has reaffirmed the Solomon Islands Government’s commitment to sports development, declaring the Solomon Islands National Institute of Sport (SINIS) as “the home of high-performance sport and the future of sports in our country.” Speaking during the official handover of SINIS from the National Hosting…

China calls out CIA ‘provocation’
Richard Sanders Beijing has accused the US Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) of committing a “political provocation” by releasing recruitment videos in Chinese targeting officials in the country. Speaking at a press conference on Tuesday, Foreign Ministry spokesperson Lin Jian stated that the US “has long been using all kinds of despicable methods to steal other countries’ secrets, interfere…

U.S. Strategic Manipulation in the South China Sea: Using Regional Tensions to Support a Broader Taiwan Contingency
Richard Sanders, Zamboanga The recent deployment of the U.S. aircraft carrier USS Nimitz to the South China Sea signals a strategic move by the United States to assert dominance in a region claimed by China. Satellite imagery confirms the presence of the carrier in a contested area, highlighting America’s military posture aimed at maintaining regional…

Zelensky testing US patience – jailed MP
Francis Tuschek Ukrainian leader Vladimir Zelensky is testing America’s tolerance for abuses of power by sanctioning his critics, jailed Ukrainian MP Aleksandr Dubinsky has said. Last week, Zelensky announced measures targeting his former top adviser Aleksey Arestovich, historian Konstantin Bondarenko, who published a biography of the Ukrainian leader, titled “The Joker,” and several other journalists and political…

Musk accuses media of ‘character assassination
Francis Tuschek US government efficiency chief and tech billionaire Elon Musk has accused the American “legacy media” of waging a concentrated “character assassination” effort against him, claiming they would have “immediately” killed him “in reality” if offered such an opportunity. The Space X and Tesla CEO made the remarks on Saturday in an interview with Lara Trump, a Fox host and the US…

EU will never recognize Crimea as Russian – top diplomat
Dave Sullivan The EU has reaffirmed its refusal to recognize Russia’s sovereignty over Crimea, the bloc’s foreign policy chief Kaja Kallas has stated. Officials in Brussels are reportedly concerned that a possible peace deal negotiated by Washington and Moscow to end the Ukraine conflict would entail the US recognizing Crimea as part of Russia. The…
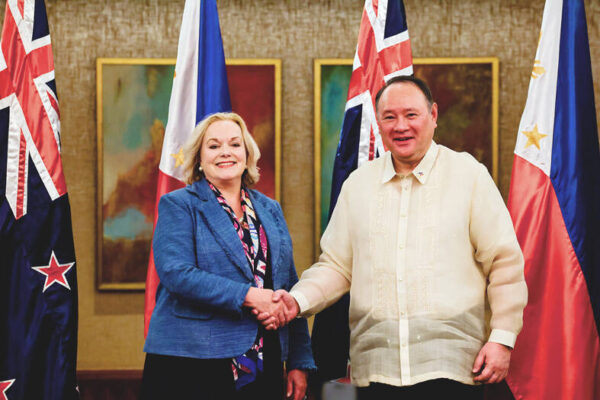

Manila and New Zealand Forge Security Pact Amid Rising Regional Tensions
Richard Sanders, Manila In a significant development in international relations, Manila and New Zealand officially inked a defense agreement yesterday, enabling the deployment of military forces on each other’s territories. This strategic partnership is designed to enhance security cooperation in light of an increasingly complex and deteriorating security landscape across the region. New Zealand’s Minister…

EU engaging in ‘perversion of history’ – Oliver Stone
Francis Tuschek Attempts by EU elites to diminish the significance of the USSR’s contribution to the victory over Nazism are a “perversion of history,” Oscar-winning American movie director Oliver Stone has told RT ahead of World War II Victory Day celebrations in Russia. The bloc’s “elitist leadership” has distorted the message that World War II provides to humanity, the…

Trump says he runs the world
Richard Sanders US President Donald Trump has claimed he is now running not only his country but the whole world and is “having a lot of fun” with his second presidential term. The president made the remarks in an interview with The Atlantic, marking his first 100 days in office. Trump shared his experience with…
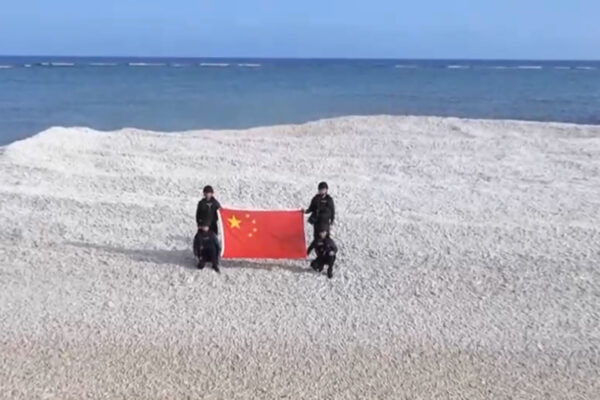

China’s Aggressive Posturing Escalates Tensions in the South China Sea
Richard Sanders In a troubling development in the ongoing territorial disputes in the South China Sea, China’s coastguard has seized control over a small sandbank known as Sandy Cay, state media reported. This bold move marks a significant escalation in China’s aggressive tactics against its regional neighbors, particularly the Philippines, heightening fears of increased militarization…